As we age, maintaining muscle strength becomes one of the most important factors for staying active, independent, and healthy. Sarcopenia, the gradual loss of muscle mass and strength, affects millions of older adults worldwide and can make everyday activities such as climbing stairs, carrying groceries, or even getting out of a chair more challenging. The encouraging news is that the right nutrients, found in everyday foods, can help slow down or even reverse some of this muscle loss. One protein-rich food in particular has shown remarkable potential for supporting muscle health and helping seniors regain energy and mobility.
In this guide, you’ll learn what makes this nutrient so powerful against sarcopenia, why it works, and how you can easily add it to your meals to improve strength, mobility, and quality of life at any age.
Understanding Sarcopenia and the Importance of Muscle Health

Sarcopenia is a natural part of aging, but its severity can be increased by inactivity, poor diet, and chronic illnesses. Research from the National Institute on Aging shows that muscle mass can decline by three to eight percent every decade after the age of 30, and the rate of loss accelerates after 60. This decline doesn’t just weaken muscles — it affects balance, mobility, and metabolism, increasing the risk of falls, fractures, and loss of independence.
Supporting muscle health through both exercise and nutrition is essential. While regular strength training stimulates muscle growth, the right nutrients provide the building blocks for repair and recovery.
Why Protein is Essential for Combating Muscle Loss
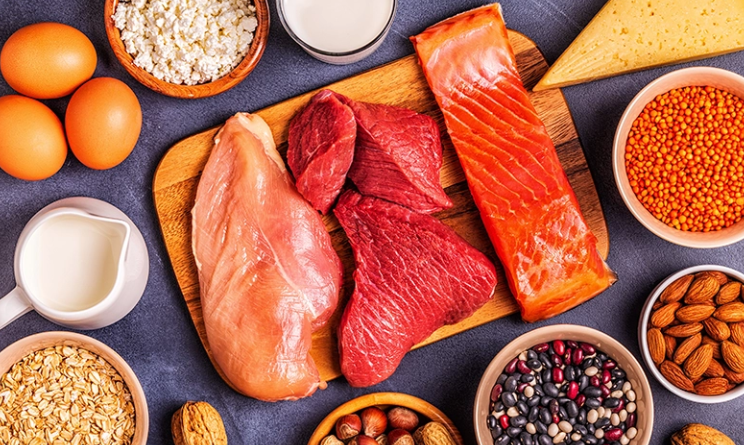

Protein is the primary nutrient responsible for building and repairing muscle tissue. For older adults, adequate protein intake is crucial to prevent and slow the effects of sarcopenia. Among the amino acids in protein, leucine stands out for its ability to activate muscle protein synthesis — the body’s process of building new muscle fibers. A diet rich in leucine and complete proteins can help maintain strength, boost recovery, and improve overall physical performance.
Why Lean Meats Stand Out for Muscle Support

Lean meats such as chicken breast, turkey, and lean cuts of beef or pork are among the best dietary sources of complete protein. They provide all the essential amino acids your body needs, including high amounts of leucine. Compared to many plant-based sources, lean meats offer a higher leucine content per serving. According to Harvard Health, a modest three-ounce serving of chicken breast contains around 2.5 grams of leucine — nearly enough to stimulate muscle growth when combined with resistance training.
Lean meats also deliver important nutrients that contribute to energy and overall health, including iron for oxygen transport, zinc for immune function, and vitamin B12 for nerve and muscle performance.
Easy Ways to Incorporate Lean Meats Into Your Diet

Adding lean meats to your meals doesn’t have to be complicated. You can enjoy grilled or baked chicken breast as a main dish, swap processed meats for lean turkey or beef, or add diced lean meat to soups, salads, or stir-fries. Preparing simple dishes like turkey chili, chicken and vegetable stir-fry, or lean beef stew can provide a nutrient-rich, satisfying meal. Aim for 20 to 30 grams of protein in each meal to maximize muscle-building benefits.
Pairing Protein with Other Muscle-Friendly Nutrients and Habits

Protein works best when supported by a complete healthy lifestyle. Combining lean meats with resistance exercises such as weightlifting or resistance bands helps muscles respond more effectively to protein intake. Adequate vitamin D is also vital for muscle function, so have your levels checked and supplement if needed. Eating a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats ensures your body gets the full spectrum of nutrients it needs. Staying hydrated is equally important, as dehydration can impair muscle performance and recovery.
Important Considerations for Older Adults

While lean meats are a powerful tool for muscle health, individuals with kidney disease or other health concerns should speak with their healthcare provider before increasing protein intake. Choosing minimally processed, low-fat cuts is best for heart health, and cooking methods such as baking, steaming, or grilling can help preserve nutritional value without adding unnecessary fat.
Taking the First Step Toward Stronger Muscles
You can start improving muscle health today by planning meals around lean meats a few times each week, pairing them with nutrient-rich vegetables and whole grains, and incorporating regular strength exercises into your routine. Over time, these simple changes can improve strength, balance, and energy, making everyday activities easier and more enjoyable.
Sarcopenia may be a natural part of aging, but with the right nutrition and habits, it doesn’t have to define your later years. Lean, protein-rich foods like chicken breast, combined with an active lifestyle, can help you stay strong, mobile, and independent for decades to come.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor before making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine.