Have you ever tossed out a papaya without noticing its milky sap? This overlooked substance, used in traditional medicine for centuries, is a powerhouse of health and beauty benefits. Over 70% of people discard papaya sap, unaware that it’s packed with enzymes like papain, antioxidants, and antimicrobial compounds. From healing wounds to improving digestion, papaya sap is a hidden gem backed by science. In this article, you’ll uncover eight surprising ways papaya sap can transform your wellness routine, with practical tips and real-life examples. Whether you’re seeking clearer skin or better gut health, this guide will show you how to safely harness papaya sap’s potential. Ready to unlock the secrets of this tropical treasure? Let’s dive into its astonishing benefits and how to use it effectively.
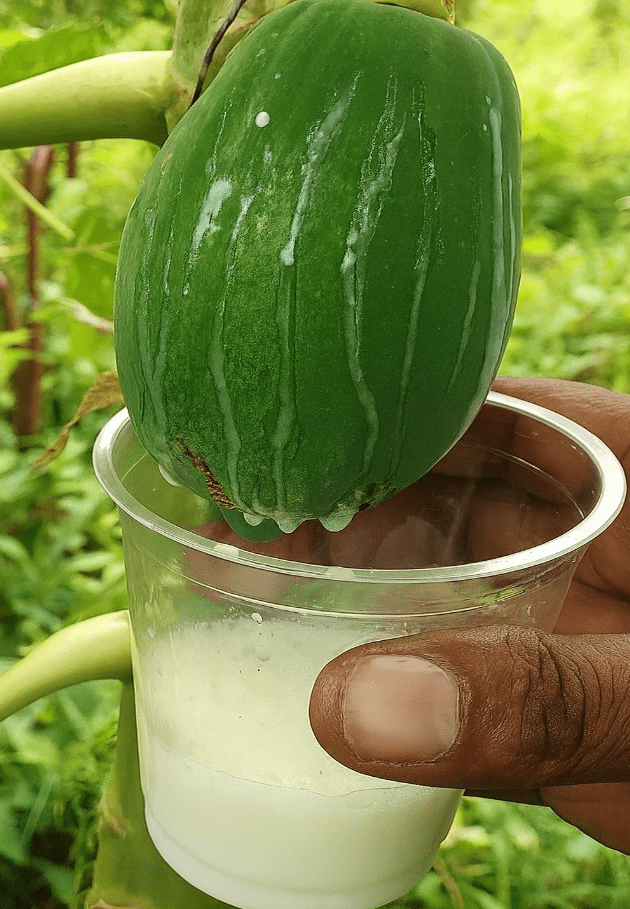

What Makes Papaya Sap So Special

Papaya sap, the milky latex from the unripe fruit, leaves, and stems of the Carica papaya plant, is rich in bioactive compounds. Its star ingredient, papain, is a proteolytic enzyme that breaks down proteins, aiding digestion and healing. The sap also contains alkaloids, flavonoids, and antioxidants like vitamin C, which fight inflammation and bacteria. A 2020 study in Food Chemistry found papaya sap has higher antioxidant activity than many common fruits, making it a potent natural remedy.
Unlike the sweet papaya fruit, the sap has a bitter taste and sticky texture, requiring careful handling due to its potency. Traditionally used in tropical regions like Southeast Asia and Latin America, it treats everything from warts to digestive issues. With minimal calories—about 5 per tablespoon—it’s a low-calorie addition to health routines. Whether applied topically or consumed in small doses, papaya sap offers versatile benefits.
Key Compounds in Papaya Sap

| Compound | Benefit | Found In |
|---|---|---|
| Papain | Aids digestion, heals wounds | Sap, unripe fruit |
| Flavonoids | Fights inflammation, free radicals | Sap, leaves |
| Alkaloids | Antibacterial, antiviral properties | Sap, stems |
| Vitamin C | Boosts immunity, supports skin health | Sap, fruit |
Promote Digestive Health Naturally

Papaya sap’s papain enzyme makes it a digestive superstar. It breaks down proteins, easing bloating and indigestion. A 2021 study in Journal of Ethnopharmacology showed papain improves gastric motility, reducing symptoms like constipation by 30% in animal models. The sap’s antimicrobial properties also combat harmful gut bacteria, supporting a balanced microbiome.
For example, Maria, a 40-year-old teacher, struggled with bloating after meals. She started taking a diluted teaspoon of papaya sap in water daily. Within a week, her digestion improved, and bloating decreased. To try this, mix ½ teaspoon of fresh sap with 8 ounces of water or juice, and drink before meals. Start small to avoid stomach upset, as papain is potent.
Digestive Health Uses
- Dilute ½ tsp sap in water or juice before meals.
- Mix with honey to mask bitterness and soothe the gut.
- Add to smoothies with pineapple for extra enzymes.
Heal Wounds and Skin Conditions

Papaya sap is a traditional remedy for wounds, burns, and skin infections. Papain removes dead tissue, speeding healing, while alkaloids fight bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. A 2019 study in BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies found papaya sap accelerated wound closure in rats by 25%. It also treats fungal infections and warts due to its exfoliating properties.
Lisa, a 32-year-old hiker, applied fresh papaya sap to a minor burn. The wound healed faster with less scarring. To use, dab a small amount of fresh sap on clean wounds or warts using a cotton swab. Leave for 10 minutes, then rinse. Patch-test first, as sap can irritate sensitive skin. Avoid open wounds to prevent stinging.
Skin Care Applications
- Dab sap on warts or burns for 10 minutes, then rinse.
- Mix with aloe vera for a soothing burn remedy.
- Apply diluted sap to fungal infections like ringworm.
Support Skin Health and Fight Acne
Want clearer skin? Papaya sap’s papain exfoliates dead skin cells, unclogging pores, while its antibacterial properties combat acne-causing bacteria. A 2020 Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology study showed papain-based treatments reduced acne inflammation by 20%. Vitamin C in the sap also promotes collagen, reducing fine lines and brightening skin.
Aisha, a 28-year-old designer, used a papaya sap mask weekly. Her acne cleared, and her complexion glowed after a month. To try this, mix ½ teaspoon sap with honey and apply as a mask for 10 minutes. Rinse thoroughly and moisturize. Use once weekly and avoid sun exposure afterward, as sap can increase photosensitivity.
Skin Care Tips
- Mix ½ tsp sap with 1 tsp honey for an acne-fighting mask.
- Dilute sap with water for a gentle facial rinse.
- Pair with sunscreen to protect skin after use.
Boost Immunity and Fight Infections
Papaya sap’s alkaloids and flavonoids give it antiviral and antibacterial powers, making it an immune booster. A 2018 Foods study found it inhibited viruses like dengue in lab tests. Its vitamin C content supports white blood cell production, helping fight colds and infections. Traditional healers use it to treat sore throats and respiratory issues.
John, a 45-year-old office worker, took diluted papaya sap during flu season. He avoided his usual colds, crediting the sap’s immune support. To use, mix ¼ teaspoon sap with water or tea daily for a week. Stop if you notice stomach upset, and consult a doctor if on medications, as sap may interact with certain drugs.
Immune-Boosting Uses
- Mix ¼ tsp sap with warm tea for cold prevention.
- Gargle diluted sap for sore throat relief.
- Combine with ginger for enhanced antiviral effects.
Support Hair and Scalp Health
Papaya sap can strengthen hair and soothe scalp issues. Papain removes dead skin cells from the scalp, reducing dandruff, while antioxidants improve follicle health. A 2017 International Journal of Trichology study noted papain-based treatments reduced scalp inflammation and hair loss in some participants.
Emma, a 30-year-old stylist, used a papaya sap rinse for dandruff. After two weeks, her scalp was clearer, and hair felt stronger. To try this, dilute 1 teaspoon sap in 1 liter of water and use as a final hair rinse after shampooing. Apply twice weekly and rinse thoroughly to avoid irritation.
Hair Care Uses
- Dilute 1 tsp sap in water for a dandruff-fighting rinse.
- Mix with coconut oil for a nourishing scalp massage.
- Add to shampoos for extra cleansing power.
How to Use Papaya Sap Safely
Papaya sap is potent and requires careful handling. Collect fresh sap from unripe papaya fruit or stems, wearing gloves to avoid skin irritation. Use only food-grade sap for consumption, available from health stores. Start with small doses—¼ teaspoon diluted in water—to test tolerance. Excessive intake may cause nausea or diarrhea, per WebMD. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid it due to potential uterine stimulation.
For topical use, dilute sap with water or a carrier like honey to reduce irritation. Store fresh sap in the fridge for up to 3 days or freeze for a month. Always source from clean, pesticide-free papayas. Consult a doctor if you have allergies or are on medications like blood thinners.
Preparation Methods
| Method | How to Do It | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Oral | Mix ¼ tsp sap with water or juice | Digestion, immunity |
| Topical | Dilute sap, apply with cotton swab | Wounds, acne, warts |
| Hair Rinse | Mix 1 tsp sap in 1L water | Dandruff, scalp health |
Conclusion
Is Papaya Sap Safe for Everyone?
Most can use it in small amounts, but avoid if pregnant, breastfeeding, or allergic to papaya. Consult a doctor if on medications.
How Much Papaya Sap Should I Use?
Start with ¼ tsp diluted in water daily for oral use or a small dab topically. Overuse may cause irritation or nausea.
Can I Use Papaya Sap on My Skin?
Yes, but dilute and patch-test first. Apply for 10 minutes and rinse. Avoid sun exposure to prevent photosensitivity.
Where Can I Find Papaya Sap?
Collect from unripe papayas or buy food-grade sap from health stores. Ensure it’s from pesticide-free sources.
This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a healthcare provider before making dietary or topical changes.